Small Screws, Big Manufacturing: How Does Intelligent Tightening Secure a Key Position in the Assembly Process?
【Introduction】 Precision machining、Robotics、Automation
Introduction:In May this year, Changchun Fengyue Branch of FAW Toyota Motor (Chengdu) Co., Ltd. announced a recall of over 10,000 domestically-produced vehicles. The reason was that the toe adjustment bolts on the lower control arms of the rear suspension might have torque tightening defects. Long-term use could cause the bolts to loosen or fall off.
Similarly, a certain brand recalled 5,128 vehicles due to "torque calibration defects of the engine cylinder head screws". Some car owners experienced loosening of the cylinder head screws while driving, leading to oil leakage, reduced power, and ultimately cylinder scuffing. The maintenance cost exceeded 20,000 yuan...
Under the ultimate requirements for product quality and safety, tightening has become a "key link" in component assembly. Especially with the increasing demands for quality and efficiency, automated and intelligent tightening is becoming more and more popular. Is this a simple replacement for traditional manual work, or a redefinition of precision and yield rate?

Why Has Intelligent Tightening Become a Must-Have?
According to industry insiders, in the first half of 2025, BYD launched a new generation of intelligent motor assembly lines at its Fudi Power base. This production line used servo electric tightening systems on a large scale for the first time, with the tightening precision of a single bolt controlled within ±3%. The tightening data is automatically uploaded to the MES system, realizing 100% quality traceability.
On the other hand, the new electric drive workshop built by Li Auto in its Qingdao new factory cooperated with Yamazen of Japan to introduce intelligent torque control tightening technology. It emphasizes the characteristics of "flexibility, traceability, and reconfigurability" to support the rapid switching of different motor models in the later stage of the production line.
In the manufacturing of new energy electric drive systems, taking the mainstream permanent magnet synchronous motor as an example, under high-speed and high-load working conditions, any tiny assembly error may lead to risks such as thermal attenuation, vibration, or even disintegration. The tightening of a small bolt is crucial for power density and yield rate, and behind it lies the overall production line integration capability, process execution, and cost control.
During the 14th Five-Year Plan period, the global intelligent tightening tool market size reached 822.60 million US dollars in 2024; it is expected to reach 1.17495 billion US dollars by 2031, with a compound annual growth rate of 5.6% from 2025 to 2031.
Behind this huge increment is the steadily expanding intelligent tightening market. Then why is everyone starting to "compete fiercely" for tightening equipment? In this process, how can local equipment manufacturers accelerate the localization replacement of tightening equipment?
Beyond Precision and Speed: What Else Needs to Be Considered?
Today's intelligent tightening systems can fundamentally reduce product failures and after-sales repairs caused by tightening problems, improve product yield and reliability, and significantly enhance production efficiency. At the same time, they need to collaborate with industrial robots, machine vision, and flexible assembly systems to cover the entire industry, including 3C electronics, new energy vehicles, energy storage, and home appliances. However, the technical challenges vary in different scenarios:
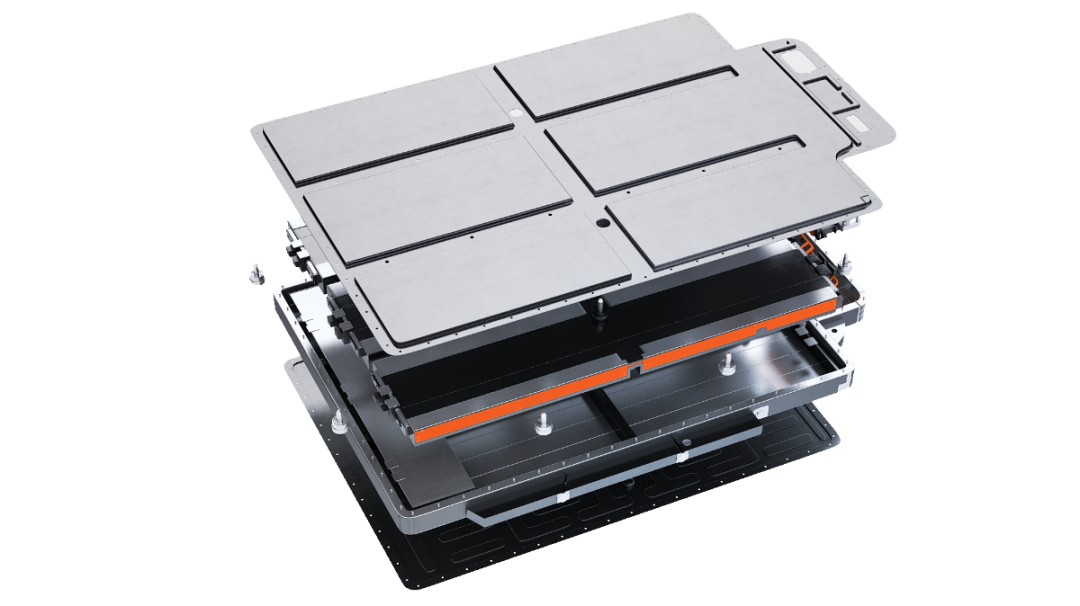
- New Energy Battery Module Assembly: The battery pack has a large volume and limited workstation space. Improper operation during vertical or horizontal tightening may lead to skewed nails or floating nails. Battery pack bolt tightening is generally defined as A/B class safety level; unqualified residual torque can easily cause screw loosening and safety failures.
- Automobile Engine & Chassis Tightening: Excessive screw length may cause misalignment with holes when fed into the tightening gun. Frequent shutdowns and restarts reduce production line efficiency, increase assembly time and labor costs, and hinder continuous operation.
- 3C Electronics Industry: Micro screws (M0.6-M1.4) with narrow torque tolerance (±0.05-0.1Nm) are widely used. Lightweight materials (magnesium-aluminum alloys, carbon fibers) require higher tightening force control. Traditional tools easily cause screw stripping or substrate damage.
- Home Appliance Industry: Traditional manual tightening has large torque fluctuations (±15%), leading to loose screws and cracked plastic parts, accounting for 38% of after-sales complaints. Detailed assembly requirements (e.g., height differences, distance limits) pose great challenges.

From this perspective, where should the application of tightening technology start to make breakthroughs?
- Precision Control: Insufficient torque causes loosening; excessive torque leads to stripping, breakage, or deformation. In micro-precision electronics, torque error must be within ±3%, and the control range can be as low as 0.1N·m.
- Speed Response: Tightening cycle affects overall efficiency. It is necessary to flexibly adjust speed according to the production line rhythm and achieve millisecond-level response while ensuring precision.
- Torque Consistency: Constant output control reduces torque fluctuation to ±2% and defect rate to below 0.02%, which is difficult for manual operations.
- Assembly Sequence: Preset sequence, torque, and angle ensure uniform stress on connecting parts, avoiding deformation and breakage.
- Intelligent Traceability: Real-time recording and uploading of tightening data enable abnormal torque alarms and missing tightening prevention, solving the problem of inaccurate manual data recording and poor traceability.
A Gathering of Elites: Where Is the Next Technical Anchor Point for Intelligent Assembly?
In the field of intelligent tightening, many enterprises such as Haihou, Dannikeer, and Haobangshou have made in-depth efforts to jointly promote the technological upgrading of assembly automation.
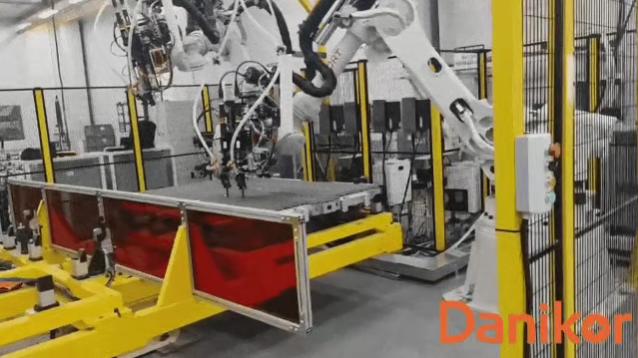
- Dannikeer: Floating tightening technology achieves multi-directional floating compensation with a standard screw jamming rate as low as 0.005%. TTC series sensor-based tools (precision 3σ±5%) ensure battery pack cycle life and safety in new energy battery PACK assembly.
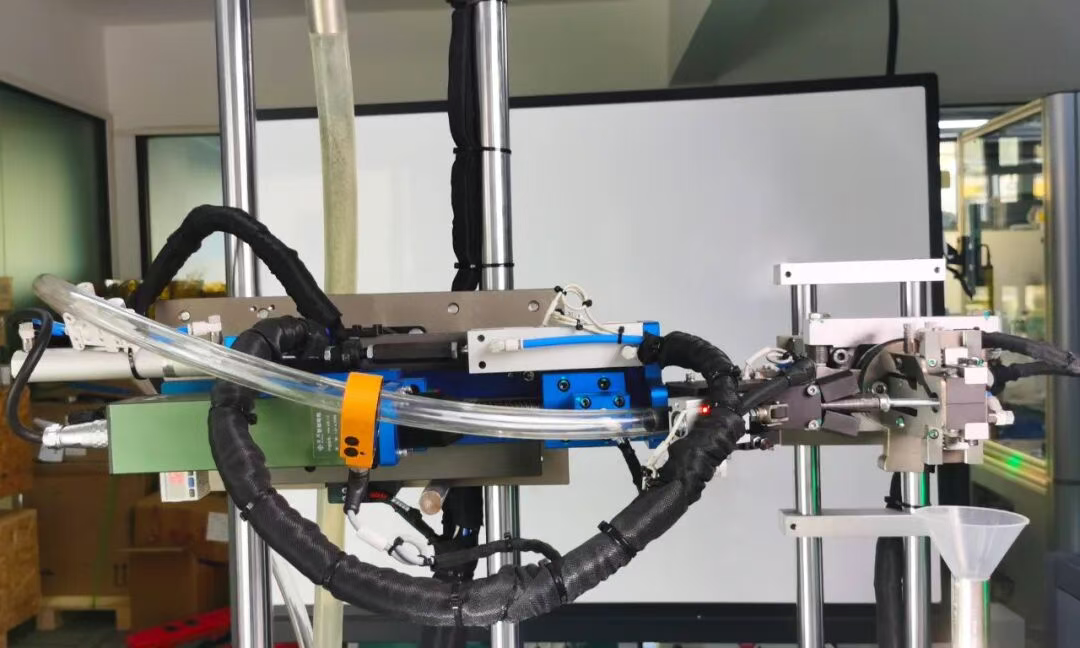
- Haihou Industry: The combination of intelligent electric screwdrivers, tightening modules, and screw feeders has a built-in high-precision torque sensor (±5% precision). It supports vertical screw delivery, automatic feeding, and is suitable for deep holes, narrow spaces, or interference areas.
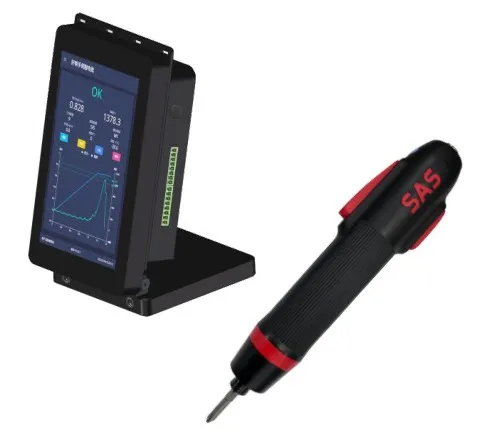

- Haobangshou: Intelligent tightening gun with 3% precision. It realizes real-time monitoring, result statistics, and MES connection. Servo automated electric screwdrivers support cross-platform wireless connection for parameter setting and result checking.
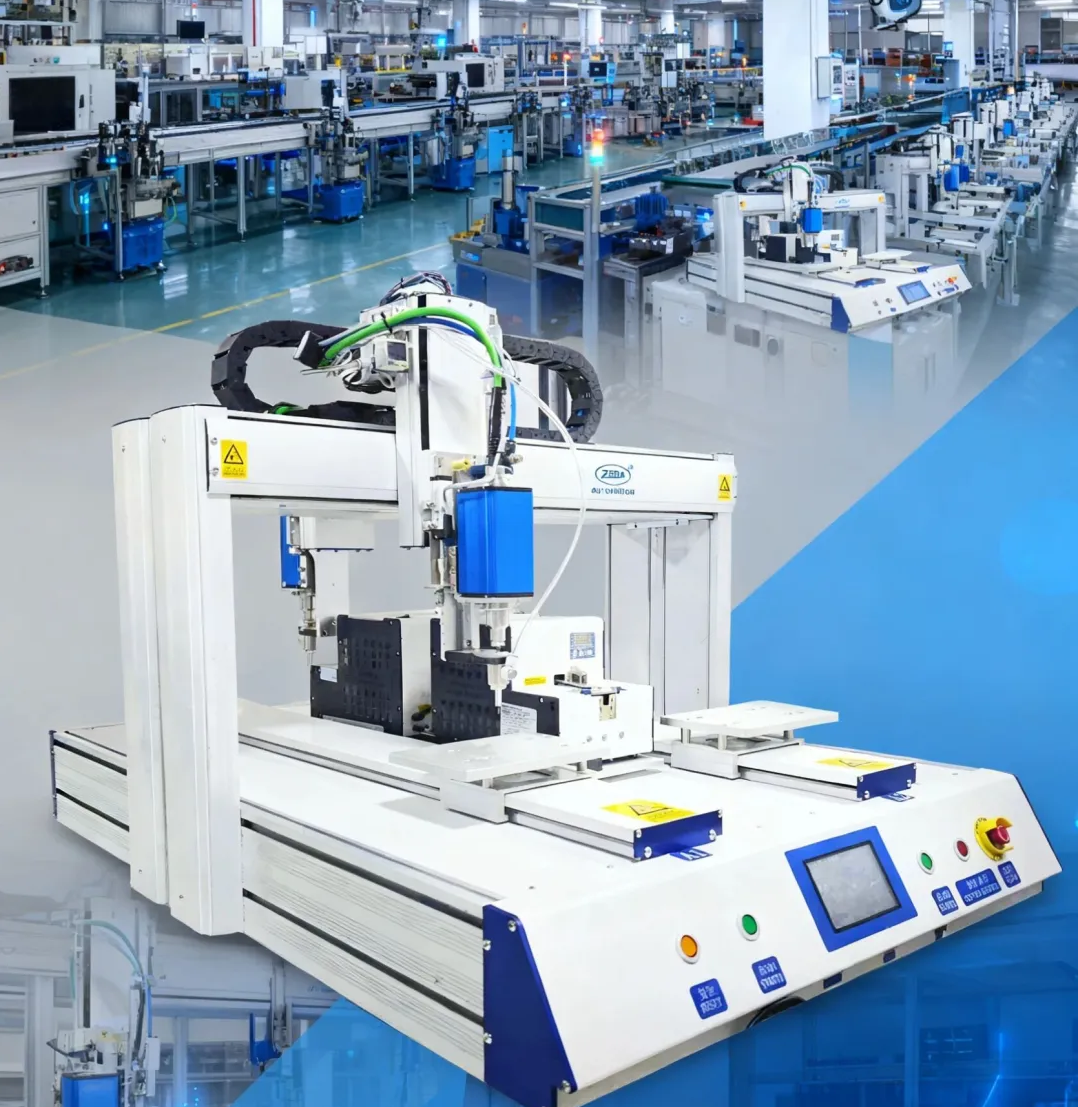

- Zeda Automation: Automatic screw machine locks up to 60 screws per minute (3-5 times more efficient than manual operation). The 0.3mm precision floating height detection and "torque + angle" dual-control mode reduce the repair rate by 85% in new energy battery pack assembly.
At the ITES Shenzhen Industrial Exhibition - Robot and Automation Equipment Exhibition to be held at the end of March next year, the above-mentioned enterprises will exhibit their latest intelligent tightening solutions. In addition, suppliers such as Feixi, Epson, Out Automation, Kilews, Rongyi, Ruike, and Hankai (covering robots, tightening, machine vision, end effectors, etc.) will also showcase their latest products to create a panorama of precision component production automation.
The Precision Component Production Automation Zone of the Robot and Automation Equipment Exhibition (a themed exhibition under ITES) focuses on assembly scenarios in precision component production. It displays automated solutions and equipment for screw locking/tightening, soldering/dispensing, press-fitting, etc., around robot assembly applications, automation equipment, and core technologies.
If you are interested in the intelligent tightening industry chain, have innovative solutions, or want to connect with leading enterprises for cooperation, scan the QR code to contact us, reserve your spot at the 2026 ITES Shenzhen Industrial Exhibition, and book prime booths now!
Do you want me to sort out a comparison table of core parameters of intelligent tightening equipment for you? It will clearly list the precision, efficiency, applicable scenarios, and other key indicators of major enterprises' products for easy comparison.