- 2026
- 2025
- 2024
- All
- Mainland China
- Taiwan China
- Hong Kong China
- Germany
- Japan
- United States
- South Korea
- Italy
- Switzerland
- Sweden





Servo drive
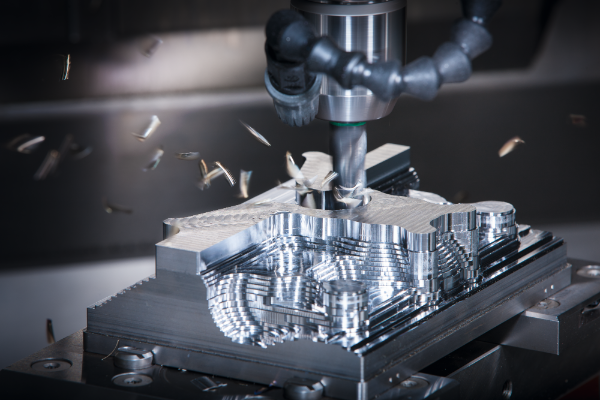
CNC lathe: good product quality, high precision, fast speed, smooth surface, smooth and smooth 3D surface contour, straight right angle, chip breaking cutting function Fine carving machine: high resolution, accurate positioning, matching moment of inertia, high overload capacity Engraving and milling machine: good speed stability, high precision, fast response frequency, wide speed range, low speed and high torque Engraving machine: fast response, good product finish, less lines, smooth curve cutting Drilling and tapping machine: high speed, low speed, high processing precision, wide adjustment range, adapt to different product requirements Machining center: rich parameter settings, cooperate to debug frequency division coefficient, inertia friction compensation, gain filtering and other parameters to complete various complex processing

Frequency converter
Our company independently develops and produces more than 100 kinds of products in 6 series of "Zhongchen" brand, covering general and special products such as frequency converters, servos, permanent magnet motors, electric vehicle drivers, etc. The voltage level is 110V-1140 V, and the power range is 0.4kW-2000 kW. The products are widely used in textile, printing, CNC machine tools, food packaging machinery, plastic machines, fans, water pumps, chemical industry, air compressors, water treatment, washing equipment, centrifuges, stone cutting equipment and other industries. We serve our customers wholeheartedly and strive to improve the level of equipment automation and meet the requirements of energy saving and environmental protection. The company has more than 80 offices at home and abroad, and its products are exported to more than 50 countries and regions such as Spain, Italy, Russia, Turkey, Egypt, India, Brazil, Canada, Thailand, Malaysia and Chile, and has gradually established and improved the global sales and service system.

US810 series pulse + bus servo
★ Diversified control functions ★ Stable and reliable operation ★ Easy to use ★ IGBT PWM sine wave ★ Support multiple Ethernet bus control ★ 0.2KW-22KW 220V/380W
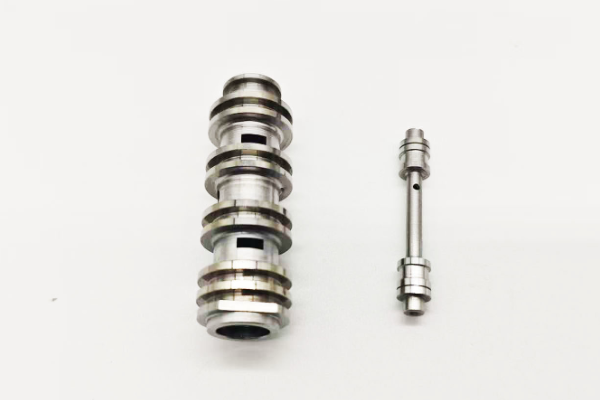


Aviation hydraulic valve sleeve
Aviation parts, high precision hydraulic valve housing, precision fit, roundness and cylindricity 0.0005mm
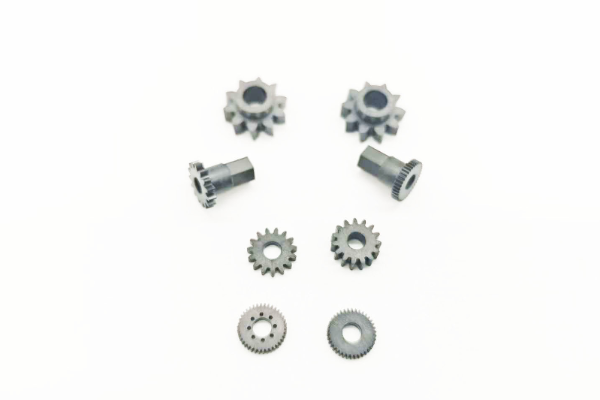

PEEK gear
High precision injection molded gears, precision ground gears, high performance materials
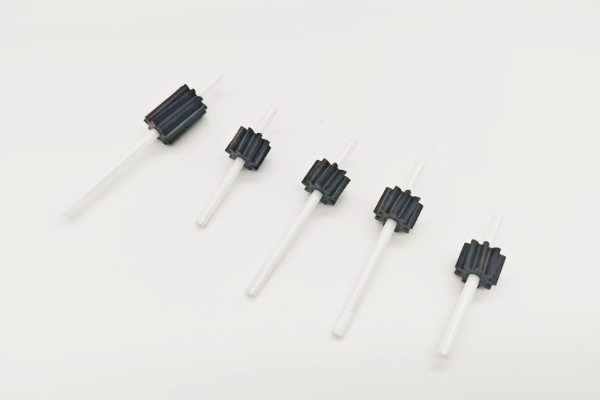
PEEK Ceramic Shaft Gear
High precision injection molded gears, precision turned gears, high performance materials
.png)
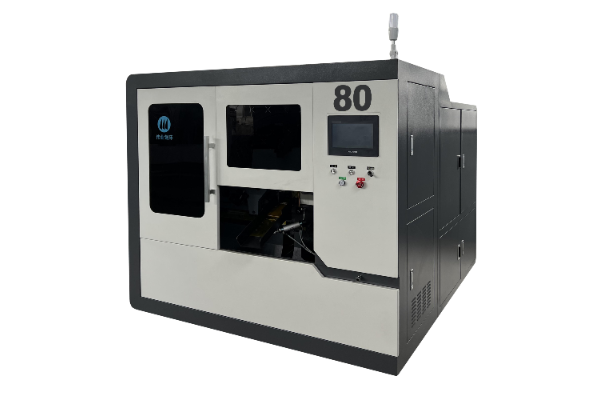

Full-automatic high-speed metal circular saw machine
WY-80 series high-speed metal circular sawing machine is a new model developed by our company in close cooperation with Zhejiang University of Technology, Chongqing University and other universities on the basis of digesting and absorbing the product characteristics of many well-known manufacturers in Japan and Taiwan. Its main parts are composed of machine tool base, cutting mechanism, anti-backlash mechanism, feeding mechanism, clamping mechanism, feeding mechanism, distributing mechanism, electric control system, hydraulic system, lubricating system, cooling system, chip cleaning mechanism, etc.
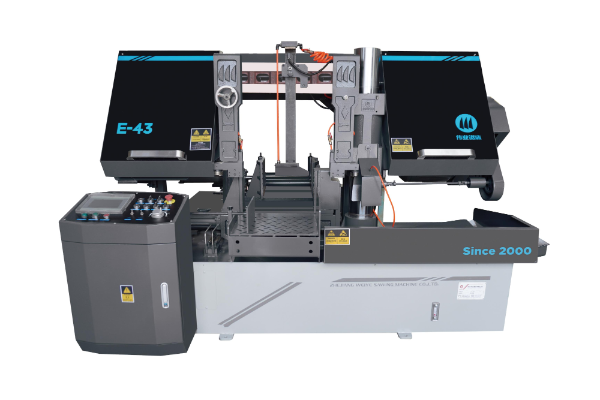

Band sawing machine
"Weiye" brand E-43 full-automatic horizontal band sawing machine is one of the series of products scientifically designed by our company, which integrates the advantages of similar products at home and abroad. With advanced PLC control, it has the characteristics of reasonable structure, stable performance, simple and reliable operation, etc. It is an ideal product with narrow incision, high efficiency, material saving and energy saving.
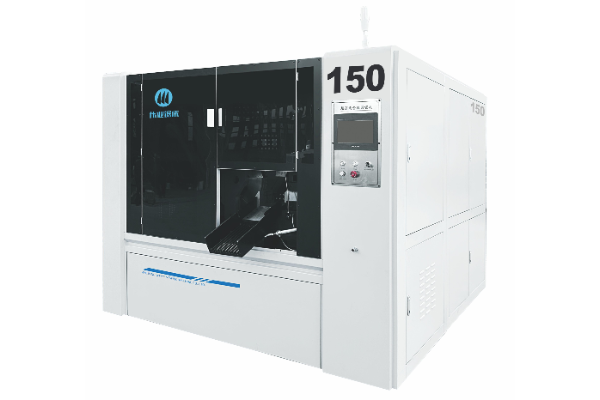

Full-automatic high-speed metal circular saw machine
WY-150 series high-speed metal circular sawing machine is a new model developed by our company in close cooperation with Zhejiang University of Technology, Chongqing University and other universities on the basis of digesting and absorbing the product characteristics of many well-known manufacturers in Japan and Taiwan. Its main parts are composed of machine tool base, cutting mechanism, anti-backlash mechanism, feeding mechanism, clamping mechanism, feeding mechanism, distributing mechanism, electric control system, hydraulic system, lubricating system, cooling system, chip cleaning mechanism, etc.
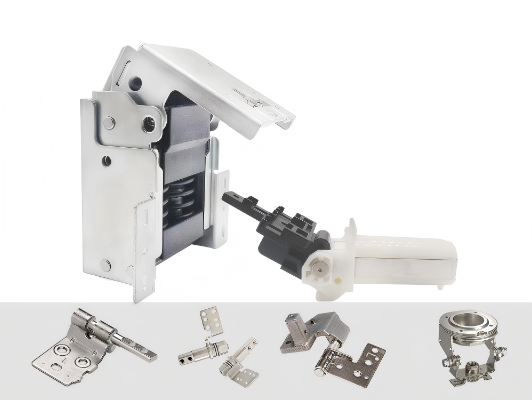


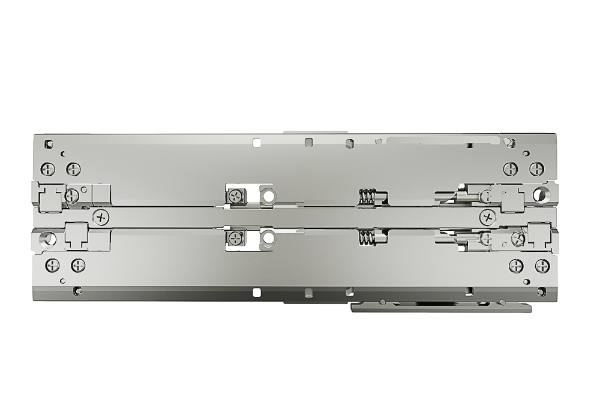
Precision hinge
We specialize in designing and manufacturing hinge products with high precision and reliability. It adopts advanced material and structure design, combined with precision machining process, to ensure that the product has excellent rotational stability, long life and light and thin characteristics. It is widely used in consumer electronics, smart home, medical equipment, automotive industry and low-altitude economy, supporting customized development and providing reliable rotation solutions for diversified application scenarios.
Folding screen mobile phone hinge
The core mechanical rotating connecting parts applied to the folding screen mobile phone adopt the current leading framework and material design scheme, use high-precision and wear-resistant liquid metal materials, as well as advanced equipment and manufacturing technology to process and produce, so as to achieve ultra-thin mobile phone body.
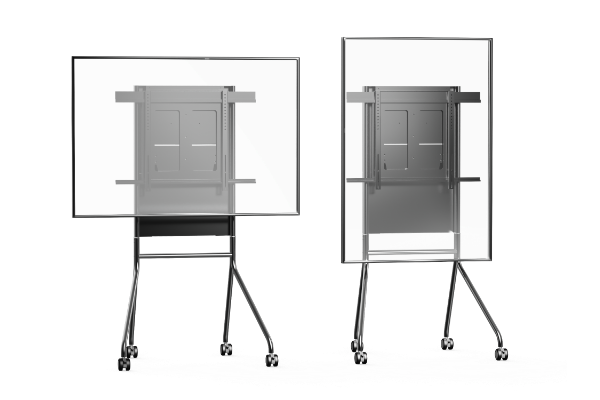
Hovering lift bracket
Hovering lifting bracket HY-XTQ003 adopts the first mechanical constant force spring balance system in China, which can be easily adjusted manually without power, and can achieve stable hovering at any position within 400 mm lifting stroke. The product offers two load specifications of 20-40 kg and 40-80 kg, which can adapt to 55-86 inch TV, conference all-in-one machine and mainstream brand display screen, and is widely compatible with various VESA standards. It has multiple safety designs such as high strength, silent operation and anti-falling, and has passed 100000 durability tests and one-year residence verification to ensure that long-term use is still stable and reliable. It is suitable for many kinds of scenes such as conference training, home audio and video, commercial exhibition, teaching and medical treatment.