Additive and Subtractive Manufacturing Together: Machining Factories Tap into Humanoid Joint Orders with New Processing Models!
【Introduction】 Precision Machining、Additive and Subtractive Manufacturing、CNC Machining、3D Printing
Introduction: What considerations go into selecting precision machining processes for humanoid robot joint structural components? How are new machining models differentiated?
Recently, XPeng’s IRON robot made a stunning debut at a launch event, striding with agile cat-like steps. Standing 178 cm tall and weighing 70 kg, this robot features 82 full-body degrees of freedom and 22 hand degrees of freedom, shedding the mechanical clumsiness of early models for a lighter, more dexterous anthropomorphic posture.
The rapid growth of the humanoid robot sector is channeling immense manufacturing demand to upstream machining industries.
The Industry Chain Sees Sustained Boom with Clear Prospects
By 2025, humanoid robots are entering the countdown to mass production, poised to reach their “iPhone moment” in 2026. Accelerated market release in the terminal market is driving explosive growth in upstream component industries.
From a domestic perspective, China’s humanoid ro
bot market size will reach 8.239 billion yuan in 2025, accounting for 50% of the global total. The market for automotive-related robots is expected to exceed 38 billion yuan, capturing one-third of the global robot industry chain’s market share. Over the next five years, humanoid robots are set to replicate the development path of new energy vehicles, emerging as a new growth pole for China’s economy.
From a global perspective, the market size of humanoid robots worldwide could reach up to $205 billion by 2035, driving a continuous surge in production capacity demand. According to the latest forecast by the International Federation of Robotics (IFR), the global market size of core components for humanoid robots will exceed $30 billion by 2025, with a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of over 25%.
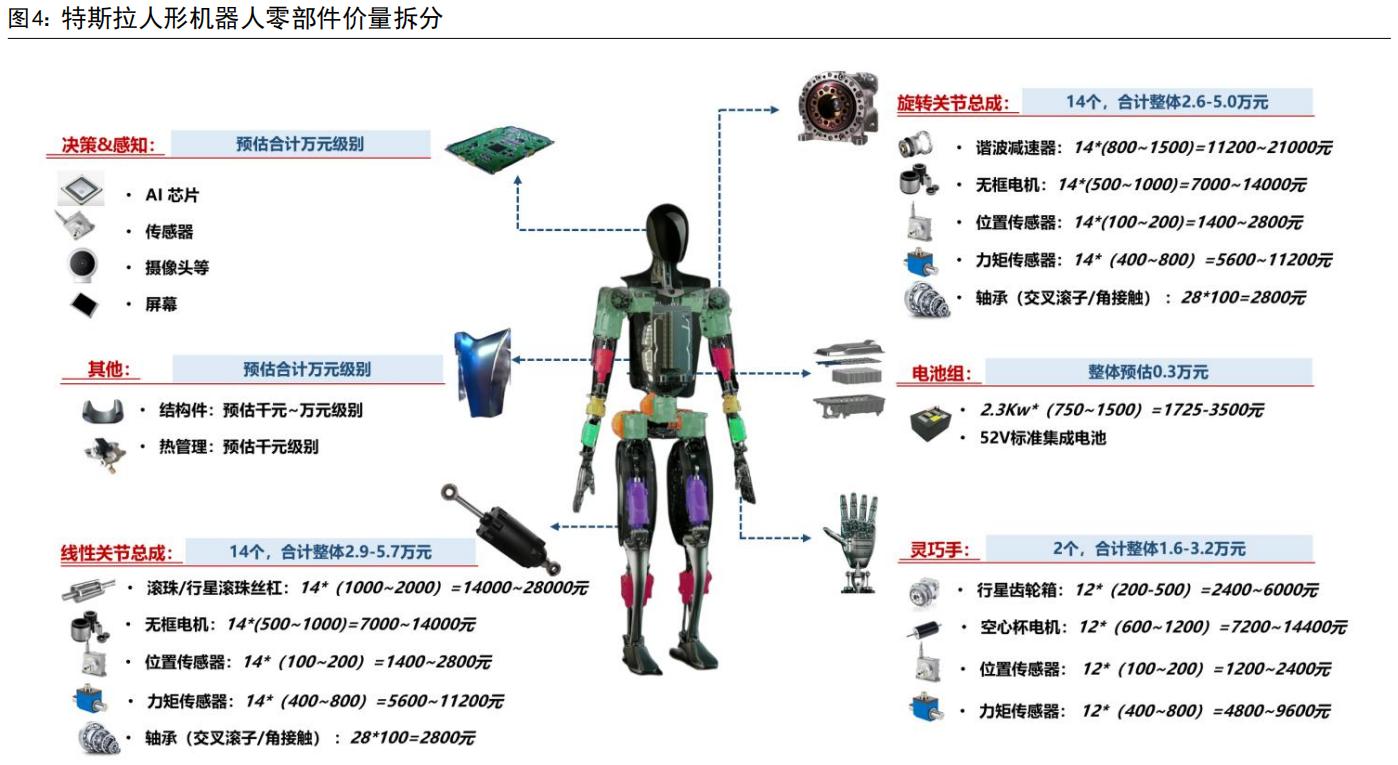
The value share of components further highlights market potential. Take a humanoid robot with a unit cost of $20,000: core components like bearings, ball screws, and sensors account for about 20% of the total cost, requiring procurement of components worth tens of thousands of yuan per unit. As commercialization advances globally, the humanoid robot component market will continue to expand, providing clear growth space for precision machining enterprises.
Machining Focuses on Joint Structural Components
Joints are the “motion core” of humanoid robots, directly determining their flexibility, stability, and anthropomorphism. A complete humanoid robot joint module consists of transmission components, drive components, support components, and sensing components—each imposing stringent requirements for precision machining.
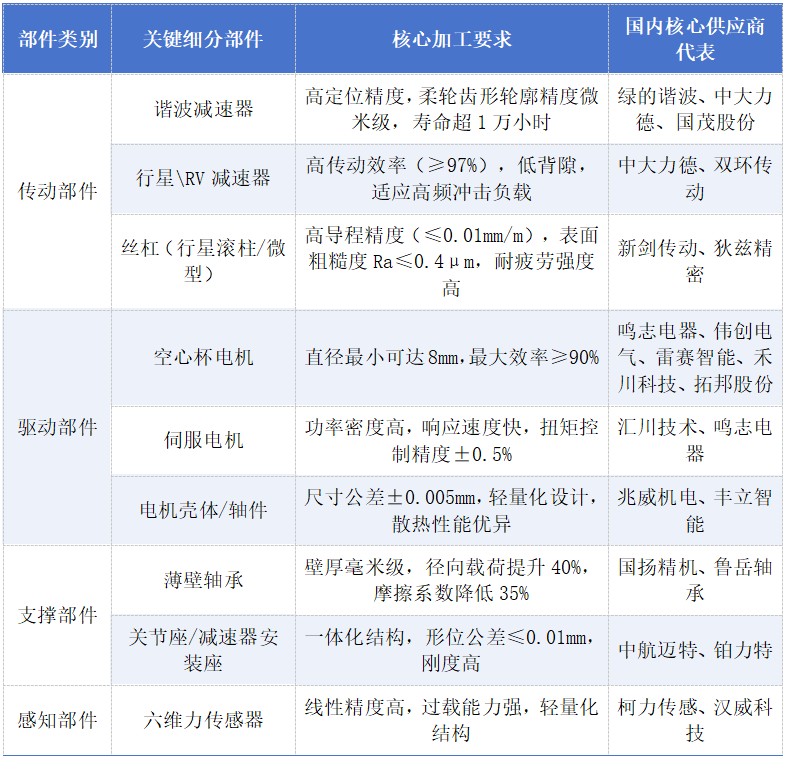
Manufacturing challenges and technological breakthroughs vary by component type:
1. Reducer Components: The flexspline of harmonic reducers uses special steel, requiring precision forging, heat treatment, and tooth profile machining. Tooth profile accuracy directly impacts transmission efficiency and lifespan. Planetary reducer gears need multi-step processes like CNC gear shaping, grinding, and honing to ensure low noise and high precision.
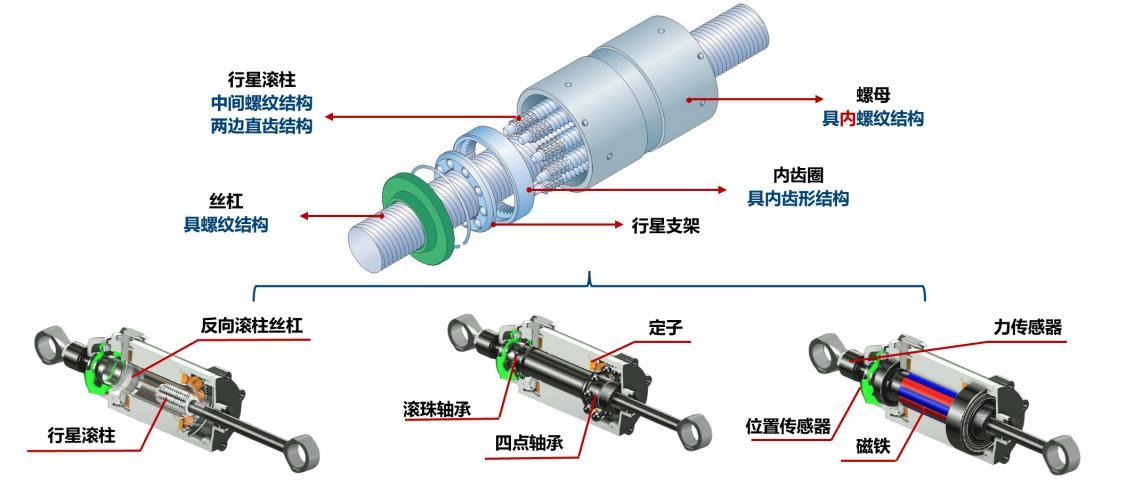

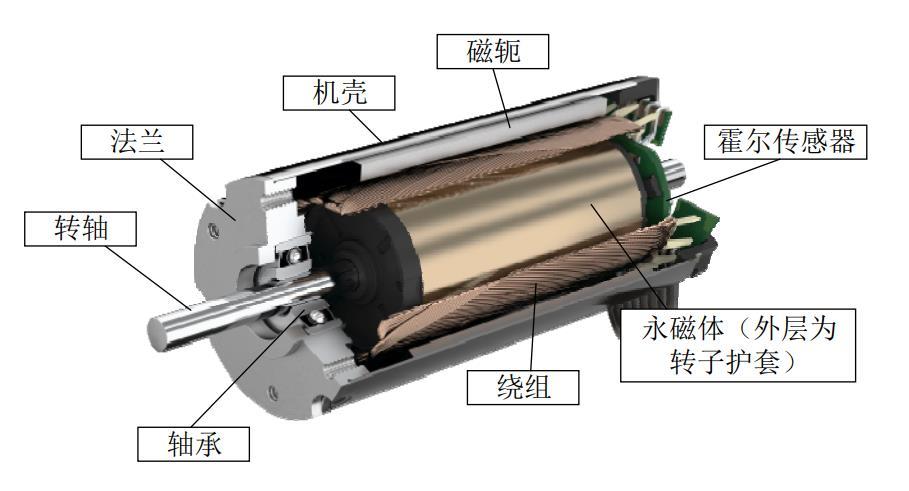
2. Motor and Bearing Components: The coreless rotor structure of hollow-cup motors is extremely difficult to machine. Moons’ Electric achieved a miniaturization breakthrough with an 8mm diameter, reaching speeds exceeding 100,000 rpm—30% faster in dynamic response than traditional motors. Joint bearings require multi-degree-of-freedom rotation within limited spaces.
3. Structural Components: Motor housings, joint bases, and similar parts must balance strength and lightweighting, often featuring complex structures designed with topology optimization. This poses huge challenges to traditional processing techniques but creates opportunities for hybrid manufacturing.
Mass production demands for humanoid robots are breaking the inertial thinking of machining enterprises. The past reliance on single CNC modes can no longer balance the three imperatives of “high performance, low cost, and fast iteration.”
Hybrid “Additive-Subtractive” Machining Models for Collaborative Manufacturing
Today, enterprises no longer depend solely on CNC machining for robot components. Instead, they organically combine additive, subtractive, forming, casting, and forging processes to leverage respective strengths, achieving a synergistic “1+1>2” effect.
First, pure CNC machining (subtractive manufacturing) uses CNC machines to remove material for all parts, simple or complex. However, in large-scale, high-efficiency, low-cost manufacturing, pure CNC suffers from low material utilization, high costs per unit for precious materials (e.g., titanium/superalloys), long processing cycles, and limited capacity expansion. Second, 3D printing is gaining traction as manufacturing costs decline, efficiency rises, and adaptability to new materials improves. Notably, the application of PEEK materials in humanoid robots allows 3D printing to reduce weight via topology optimization and lower costs—critical for flexibility.
According to Silicon Tribe Robotics, their POPPY robot, made with 3D printing, costs one-third less than traditional models.Metal 3D printing enables integrated forming of multiple parts, simplifying assembly and enhancing structural rigidity.
Third, die-casting + CNC offers an optimal balance of mass production costs and division of labor. In mass production, die-casting first produces near-net-shape blanks (castings/forgings), followed by CNC for precision machining. This model addresses the low efficiency and high cost of pure CNC in mass production while avoiding the precision limitations of single die-casting.
For example, motor housings produced via die-casting are then precision-machined on key areas (mounting surfaces, shaft holes) with five-axis CNC, ensuring dimensional consistency and cutting production costs by ~50%—perfectly meeting humanoid robot mass production needs.
The shift from pure CNC to hybrid manufacturing is essentially an industrial upgrade: from “pursuing single precision” to “achieving comprehensive optimization of performance, efficiency, and cost.”
Shared Fundamental Logic in Component Machining
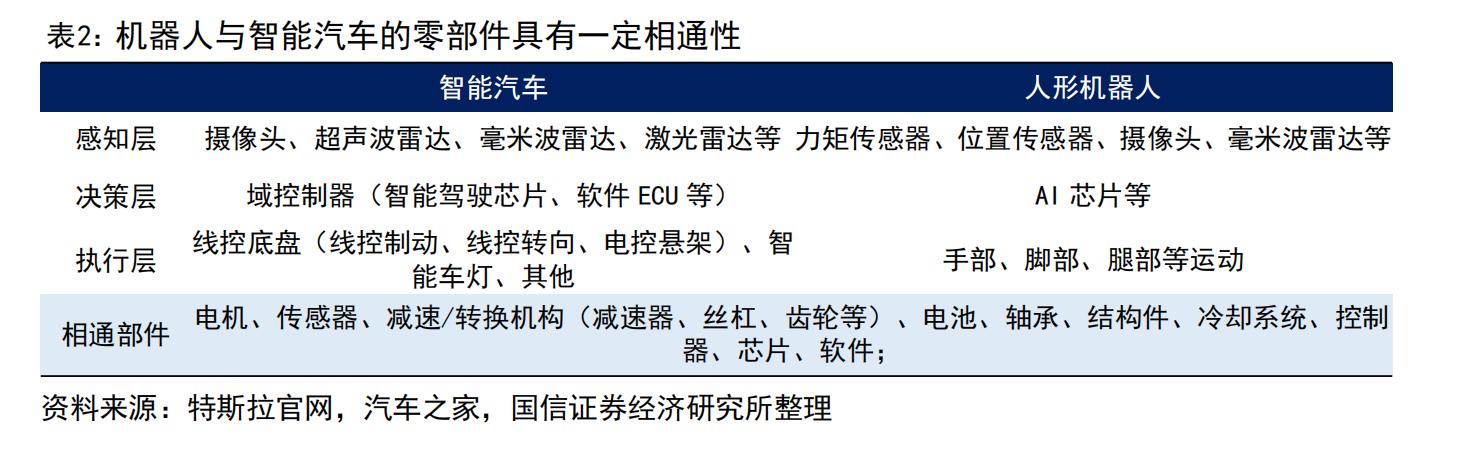
There is high commonality between automotive and robotic component manufacturing. Some robot components share fundamental manufacturing logic with auto parts in terms of materials, processes, equipment, and cost control—creating upgrading opportunities for motors, reducers, ball screws, etc. Enterprises can transfer their auto component manufacturing experience to humanoid robot core component production.
According to ITES’ field research:
· In the precision component sector, enterprises (e.g., Donghui Precision, Zhongdian Aihua, Jinzhijie, etc.) use ultra-precision CNC machining or overlay die-casting and 3D printing for dexterous hand components, joint shafts, etc., consolidating technical foundations and balancing efficiency with cost-effectiveness.
· Among them, Zhongyi Precision leveraged the ITES platform to secure orders for humanoid robot motors and housings, entering the smart equipment track.
It is worth mentioning that these enterprises (along with others like Tongxiang, Jiaye, Chenxing, etc.) will showcase relevant solutions at the 2026 ITES Shenzhen Industrial Exhibition next March. They will gather again in Shenzhen—stay tuned!
ITES Shenzhen Industrial Exhibition’s Thematic Show—Precision Component Design and Manufacturing Show: This show comprehensively displays core elements for the full chain of precision component manufacturing, covering original R&D/design, manufacturing/production, surface treatment, and contract manufacturing. It serves industries including AI smart hardware, embodied intelligence, new energy vehicles, aerospace, semiconductor equipment, and high-end medical devices, supporting localization upgrades of supply chains and high-precision component demands. (Click “Read More” at the end for details on more thematic zones~)
At that time, end buyers like UBTECH, Leju Intelligence, Lingyi iTech, Lansi Robotics, Dreame Technology, XPeng Motors, StarDust Intelligence, and iFLYTEK will be present. If you are also interested in the humanoid robot industry chain, have innovative processing solutions, and wish to engage with industry leaders to explore cooperation, welcome to scan the QR code to contact us. Secure your spot at the 2026 ITES Shenzhen Industrial Exhibition and book prime exhibition spaces now!





